A mutation that caused loss of inner hair cells within the organ of corti would cause Info
Home » Hair loss » A mutation that caused loss of inner hair cells within the organ of corti would cause Info
Your A mutation that caused loss of inner hair cells within the organ of corti would cause images are available in this site. A mutation that caused loss of inner hair cells within the organ of corti would cause are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the A mutation that caused loss of inner hair cells within the organ of corti would cause files here. Find and Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for a mutation that caused loss of inner hair cells within the organ of corti would cause pictures information linked to the a mutation that caused loss of inner hair cells within the organ of corti would cause interest, you have come to the right blog. Our site always gives you suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
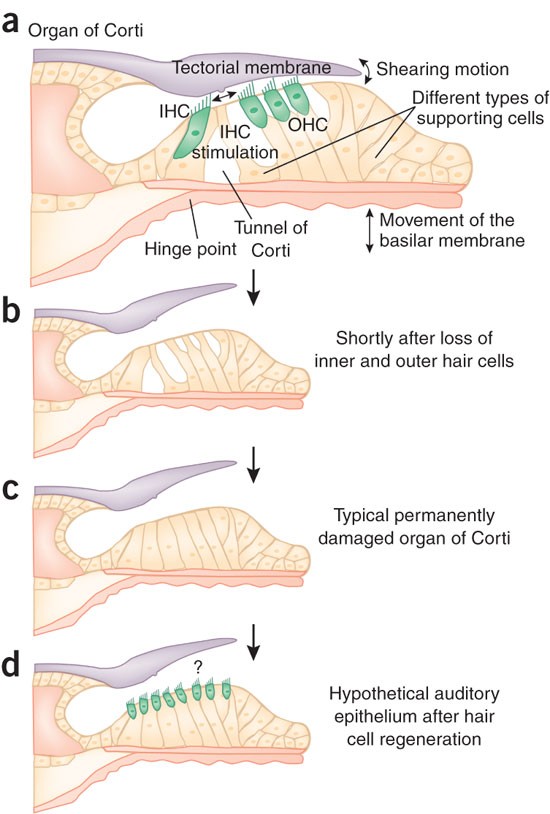
A Mutation That Caused Loss Of Inner Hair Cells Within The Organ Of Corti Would Cause. As the waves move inside the cochlea they cause other structures to move and this eventually causes hair cells that are part of the Organ of. In summary we generated Tric mice that suffer an early-onset rapidly progressive hearing loss associated with the degeneration of cochlear HCs likely due to the disruption of the epithelial barrier function in the organ of Corti. Situated near the inner hair cells of neonatal mice the GER undergoes a wave of apoptosis after postnatal day 8 P8. The inability to detect differences between different musical instruments.
 Quo Vadis Hair Cell Regeneration Nature Neuroscience From nature.com
Quo Vadis Hair Cell Regeneration Nature Neuroscience From nature.com
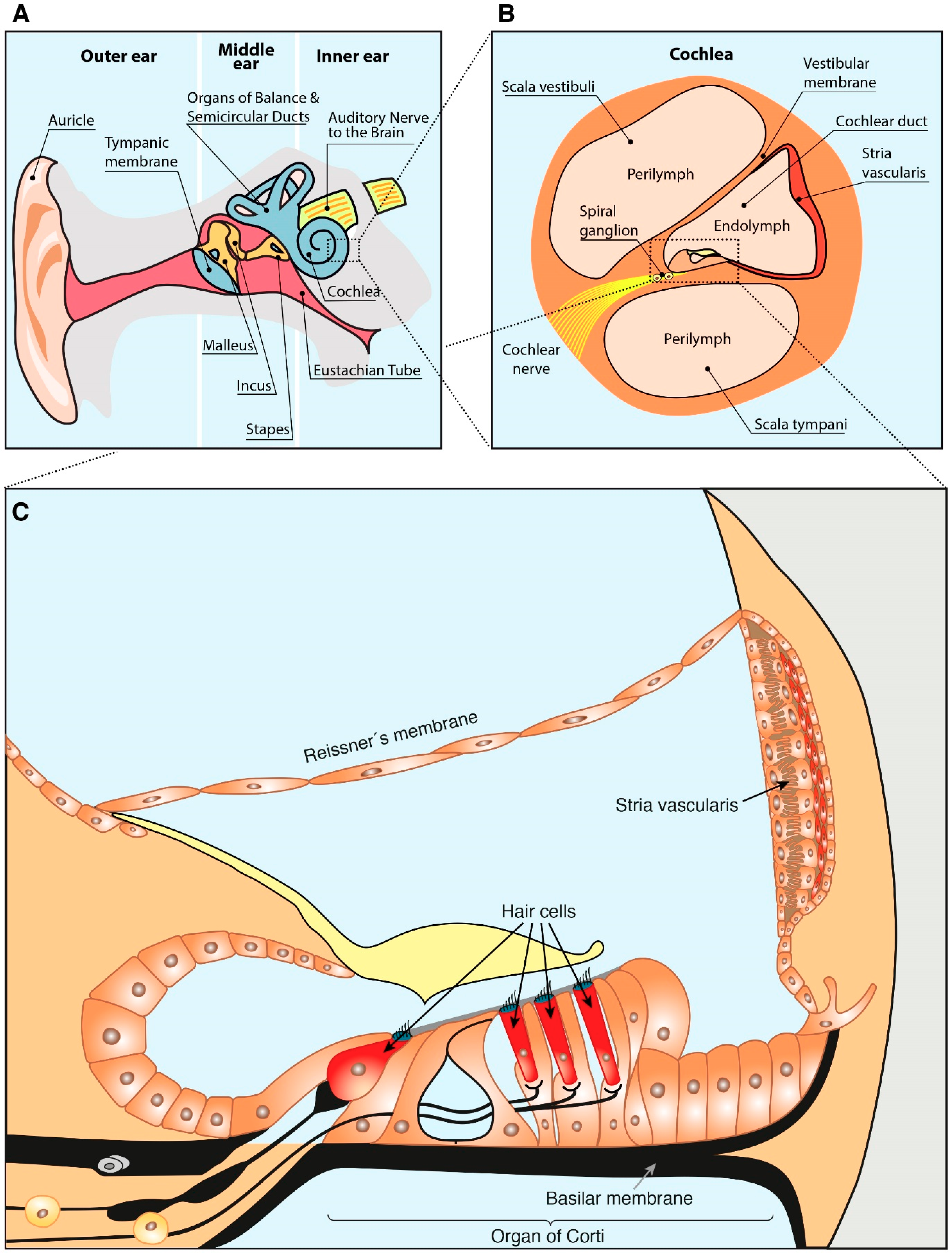
Specifically the cochlear duct growth and the formation of hair cells within the organ of Corti. A mutation that caused loss of inner hair cells within the Organ of Corti would cause. Because hearing loss was the only pathological phenotype detected in our study and the loss of HCs was the unique morphological change observed in Tric mice we. EP is generated in the stria vascularis an isolated compartment facing endolymphatic and perilymphatic spaces 5 6. Identify mutations in an alternative splice regulator ESRP1 in a family with hearing loss. The inner ear is one of the tissues with a relatively high energy demand which is supported by the finding that selected mtDNA mutationssuch as the m1555AG mutation in the mitochondrial 12S rRNA gene MIM 500008 or mutations in the tRNA Ser gene MIM 590080cause nonsyndromic hearing impairment.
Microtubules within the inner pillar cells is significantly re-duced.
The inner ear is one of the tissues with a relatively high energy demand which is supported by the finding that selected mtDNA mutationssuch as the m1555AG mutation in the mitochondrial 12S rRNA gene MIM 500008 or mutations in the tRNA Ser gene MIM 590080cause nonsyndromic hearing impairment. Atoh1 -CKO mice display a complete loss of hair cells within three weeks after birth due to the self-termination of Atoh1 expression 15. In summary we generated Tric mice that suffer an early-onset rapidly progressive hearing loss associated with the degeneration of cochlear HCs likely due to the disruption of the epithelial barrier function in the organ of Corti. Difficulty in locating the source of a sound. The inner ear defect is mainly associated with an increased number of pillar cells or modified supporting cells in the organ of Corti. Deafness has also been associated with loss of hair cells and one therapeutic approach is to find ways to regenerate the hair cells.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In summary we generated Tric mice that suffer an early-onset rapidly progressive hearing loss associated with the degeneration of cochlear HCs likely due to the disruption of the epithelial barrier function in the organ of Corti. We used this mouse model to determine whether absence of hair cells and the organ of Corti would affect development function and survival of the stria. CLDN14 mutations are a common cause of recessive hearing loss in the Pakistani population as mutations of this gene account for 225 18 of 800 families. Difficulty in locating the source of a sound. Because hearing loss was the only pathological phenotype detected in our study and the loss of HCs was the unique morphological change observed in Tric mice we.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
Situated near the inner hair cells of neonatal mice the GER undergoes a wave of apoptosis after postnatal day 8 P8. The inner ear is one of the tissues with a relatively high energy demand which is supported by the finding that selected mtDNA mutationssuch as the m1555AG mutation in the mitochondrial 12S rRNA gene MIM 500008 or mutations in the tRNA Ser gene MIM 590080cause nonsyndromic hearing impairment. As the waves move inside the cochlea they cause other structures to move and this eventually causes hair cells that are part of the Organ of. Data on mutations in PCP genes in the vertebrate suggest that the loss of individual PCP proteins differentially affects hair cells within an epithelium and hair cells between epithelia. We evaluated the GER from P8 to P12 in transgenic mice that carry the R75Wmutation a dominant-negative mutation of human gap junction protein beta 2 26 kDa GJB2 also known as connexin 26 or CX26.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
CLDN14 mutations are a common cause of recessive hearing loss in the Pakistani population as mutations of this gene account for 225 18 of 800 families. Hearing loss in the Fgfr3 Y367C mouse model demonstrates the crucial role of Fgfr3 in the development of the inner ear and provides novel insight on the biological consequences of FGFR3 mutations in chondrodysplasia. Mutations in the genes expressed in or near the organ of Corti before the differentiation of hair cells will result in a disruption in the differentiation and potential malfunction of the organ of Corti. 95 CI 1435 of deafness in the. By the end of treatment there were fewer outer hair cells than seen in an untreated cochlea because progenitors could not mature into outer hair cells.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Data on mutations in PCP genes in the vertebrate suggest that the loss of individual PCP proteins differentially affects hair cells within an epithelium and hair cells between epithelia. By the end of treatment there were fewer outer hair cells than seen in an untreated cochlea because progenitors could not mature into outer hair cells. A similar type of process occurs in the cochlea. Microtubules within the inner pillar cells is significantly re-duced. 95 CI 1435 of deafness in the.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
These results indicate that the hearing loss in patients with Otoamutations is caused by a defect in inner hair cell stimulation and reveal the limbal attachment of the TM plays a. Difficulty in locating the source of a sound. Deafness has also been associated with loss of hair cells and one therapeutic approach is to find ways to regenerate the hair cells. EP is generated in the stria vascularis an isolated compartment facing endolymphatic and perilymphatic spaces 5 6. Situated near the inner hair cells of neonatal mice the GER undergoes a wave of apoptosis after postnatal day 8 P8.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Atoh1 -CKO mice display a complete loss of hair cells within three weeks after birth due to the self-termination of Atoh1 expression 15. Clinical significance Hearing loss. Defects in these connexin proteins due to mutation are the basis of a major inherited form of deafness while other inherited forms of deafness may be associated with other components of the organ of Corti. The SLC17A8 solute carrier family 17 member 8 gene encodes vesicular glutamate transporter 3 VGLUT3 and among its isoforms VGLUT1-3 only VGLUT3 is expressed selectively in the inner hair cells IHCs. One of the causes of sensorineural hearing loss SNHL is degeneration of the inner hair cells in the organ of Corti in the cochlea.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
HCs in the organ of Corti which is. Hearing loss in the Fgfr3 Y367C mouse model demonstrates the crucial role of Fgfr3 in the development of the inner ear and provides novel insight on the biological consequences of FGFR3 mutations in chondrodysplasia. As the waves move inside the cochlea they cause other structures to move and this eventually causes hair cells that are part of the Organ of. Data on mutations in PCP genes in the vertebrate suggest that the loss of individual PCP proteins differentially affects hair cells within an epithelium and hair cells between epithelia. A similar type of process occurs in the cochlea.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
The SLC17A8 solute carrier family 17 member 8 gene encodes vesicular glutamate transporter 3 VGLUT3 and among its isoforms VGLUT1-3 only VGLUT3 is expressed selectively in the inner hair cells IHCs. The inner ear is one of the tissues with a relatively high energy demand which is supported by the finding that selected mtDNA mutationssuch as the m1555AG mutation in the mitochondrial 12S rRNA gene MIM 500008 or mutations in the tRNA Ser gene MIM 590080cause nonsyndromic hearing impairment. By the end of treatment there were fewer outer hair cells than seen in an untreated cochlea because progenitors could not mature into outer hair cells. All of the above are correct. In summary we generated Tric mice that suffer an early-onset rapidly progressive hearing loss associated with the degeneration of cochlear HCs likely due to the disruption of the epithelial barrier function in the organ of Corti.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Data on mutations in PCP genes in the vertebrate suggest that the loss of individual PCP proteins differentially affects hair cells within an epithelium and hair cells between epithelia. Atoh1 -CKO mice display a complete loss of hair cells within three weeks after birth due to the self-termination of Atoh1 expression 15. Situated near the inner hair cells of neonatal mice the GER undergoes a wave of apoptosis after postnatal day 8 P8. By the end of treatment there were fewer outer hair cells than seen in an untreated cochlea because progenitors could not mature into outer hair cells. The inability to detect differences between different musical instruments.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
The inability to detect differences between different musical instruments. Deafness has also been associated with loss of hair cells and one therapeutic approach is to find ways to regenerate the hair cells. These results indicate that the hearing loss in patients with Otoamutations is caused by a defect in inner hair cell stimulation and reveal the limbal attachment of the TM plays a. By the end of treatment there were fewer outer hair cells than seen in an untreated cochlea because progenitors could not mature into outer hair cells. The inability to detect differences in sound intensity.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
As the waves move inside the cochlea they cause other structures to move and this eventually causes hair cells that are part of the Organ of. We used this mouse model to determine whether absence of hair cells and the organ of Corti would affect development function and survival of the stria. The inner ear defect is mainly associated with an increased number of pillar cells or modified supporting cells in the organ of Corti. Difficulty in locating the source of a sound. Atoh1 -CKO mice display a complete loss of hair cells within three weeks after birth due to the self-termination of Atoh1 expression 15.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In summary we generated Tric mice that suffer an early-onset rapidly progressive hearing loss associated with the degeneration of cochlear HCs likely due to the disruption of the epithelial barrier function in the organ of Corti. Deafness has also been associated with loss of hair cells and one therapeutic approach is to find ways to regenerate the hair cells. Specifically the cochlear duct growth and the formation of hair cells within the organ of Corti. Hearing loss in the Fgfr3 Y367C mouse model demonstrates the crucial role of Fgfr3 in the development of the inner ear and provides novel insight on the biological consequences of FGFR3 mutations in chondrodysplasia. By the end of treatment there were fewer outer hair cells than seen in an untreated cochlea because progenitors could not mature into outer hair cells.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
These results indicate that the hearing loss in patients with Otoamutations is caused by a defect in inner hair cell stimulation and reveal the limbal attachment of the TM plays a. Mutations in the genes expressed in or near the organ of Corti before the differentiation of hair cells will result in a disruption in the differentiation and potential malfunction of the organ of Corti. Defects in these connexin proteins due to mutation are the basis of a major inherited form of deafness while other inherited forms of deafness may be associated with other components of the organ of Corti. Atoh1 -CKO mice display a complete loss of hair cells within three weeks after birth due to the self-termination of Atoh1 expression 15. 95 CI 1435 of deafness in the.
 Source: degruyter.com
Source: degruyter.com
Loss of Esrp1 in mice leads to morphological defects in inner ear development and cell fate switches in the lateral cochlear wall caused by altered Fgfr2 splicing patterns and Fgf ligand usage. Atoh1 -CKO mice display a complete loss of hair cells within three weeks after birth due to the self-termination of Atoh1 expression 15. In summary we generated Tric mice that suffer an early-onset rapidly progressive hearing loss associated with the degeneration of cochlear HCs likely due to the disruption of the epithelial barrier function in the organ of Corti. We used this mouse model to determine whether absence of hair cells and the organ of Corti would affect development function and survival of the stria. CLDN14 mutations are a common cause of recessive hearing loss in the Pakistani population as mutations of this gene account for 225 18 of 800 families.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Mutations in the genes expressed in or near the organ of Corti before the differentiation of hair cells will result in a disruption in the differentiation and potential malfunction of the organ of Corti. As the waves move inside the cochlea they cause other structures to move and this eventually causes hair cells that are part of the Organ of. A similar type of process occurs in the cochlea. 95 CI 1435 of deafness in the. These results indicate that the hearing loss in patients with Otoamutations is caused by a defect in inner hair cell stimulation and reveal the limbal attachment of the TM plays a.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Situated near the inner hair cells of neonatal mice the GER undergoes a wave of apoptosis after postnatal day 8 P8. Defects in these connexin proteins due to mutation are the basis of a major inherited form of deafness while other inherited forms of deafness may be associated with other components of the organ of Corti. A similar type of process occurs in the cochlea. Data on mutations in PCP genes in the vertebrate suggest that the loss of individual PCP proteins differentially affects hair cells within an epithelium and hair cells between epithelia. Deafness has also been associated with loss of hair cells and one therapeutic approach is to find ways to regenerate the hair cells.
 Source: x-mol.com
Source: x-mol.com
In summary we generated Tric mice that suffer an early-onset rapidly progressive hearing loss associated with the degeneration of cochlear HCs likely due to the disruption of the epithelial barrier function in the organ of Corti. They thus suggested that hearing loss in people with TGFBR1 mutations could be due to impaired outer hair cell formation during development. Difficulty in locating the source of a sound. These results indicate that the hearing loss in patients with Otoamutations is caused by a defect in inner hair cell stimulation and reveal the limbal attachment of the TM plays a. Loss of Esrp1 in mice leads to morphological defects in inner ear development and cell fate switches in the lateral cochlear wall caused by altered Fgfr2 splicing patterns and Fgf ligand usage.
 Source: maciverlab.bms.ed.ac.uk
Source: maciverlab.bms.ed.ac.uk
A similar type of process occurs in the cochlea. 95 CI 1435 of deafness in the. As the waves move inside the cochlea they cause other structures to move and this eventually causes hair cells that are part of the Organ of. Clinical significance Hearing loss. These results indicate that the hearing loss in patients with Otoamutations is caused by a defect in inner hair cell stimulation and reveal the limbal attachment of the TM plays a.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title a mutation that caused loss of inner hair cells within the organ of corti would cause by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.

Category
Related By Category
- Kenalog for hair loss Information
- Does wearing wigs cause hair loss Info
- Klorane anti hair loss treatment review Info
- Chris brown hair loss Resolve
- Salman khan hair loss Info
- Hair extensions for hair loss Info
- Black men hair loss Information
- Hair loss ads Information
- Ds hair loss treatment Info
- Pantene hair loss treatment Resolve
